Abbreviations, What Do They Mean?
These are some of the most common flexible packaging material acronyms
- ALU - Aluminium Foil
- BOPE - Biaxially Oriented Polyethylene
- BOPP - Biaxially Oriented polypropylene
- CA - Cellulose acetate
- CPP - Cast polypropylene
- HDPE - High Density Polyethylene
- KRAFT - Paper
- LDPE - Low Density Polyethylene
- LLDPE - Linear Low Density Polyethylene
- MCPP - Metalized cast polypropylene
- MOPP - Metalized Oriented polypropylene
- OPP - Oriented polypropylene
- PA - Nylon
- PE - Polyethylene
- PET - Polyethylene Terephthalate (aka Polyester)
- PLA - Polylactic acid
- PVC - Polyvinyl chloride
- SPE - Special Heat Resistant Polyethylene
- VM-PET - Vacuum metallised Polyester
What is Flexible Packaging?
“flexible packaging is any package or any part of a package whose shape can be readily changed.” - Flexible Packaging Association
Some of the most common examples of flexible packaging include bags, pouches, shrink films, tubes, and sleeves.

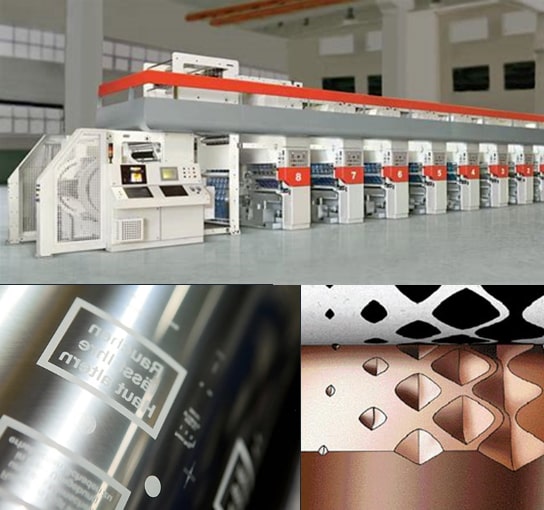
What is Gravure Printing?
Rotogravure utilises Copper plated steel cylinders which are laser photoengraved and hold the ink ready for transfer to the substrate.
Because gravure is capable of transferring more ink to the substrate than most other printing processes i.e. Flexographic, Offset it is noted for its remarkable density range (light to shadow / vignette) and hence is a process of choice for high quality image reproduction.

What is Flexographic Printing?
Flexographic (Flexo) printing was developed as a cheaper alternative to Gravure.
Flexo uses a light sensitive polymer to make a plate. Film negative is placed over the plate, which is exposed to ultra-violet light. The polymer hardens where light passes through the film and the remaining areas are washed off. Laser engraving can be used as an alternative to the above to the same effect.
The finished plates are taped / mounted onto a print sleeve or cylinder. Similar to Gravure, each plate, will represent a colour used.
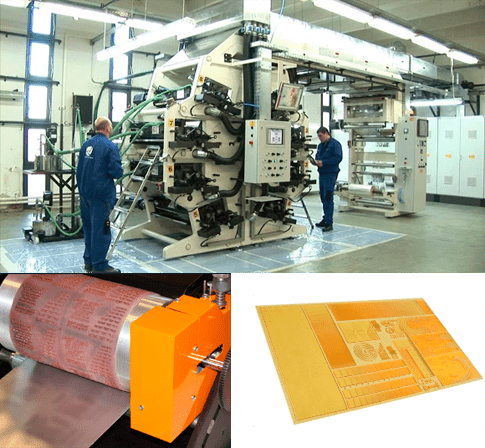
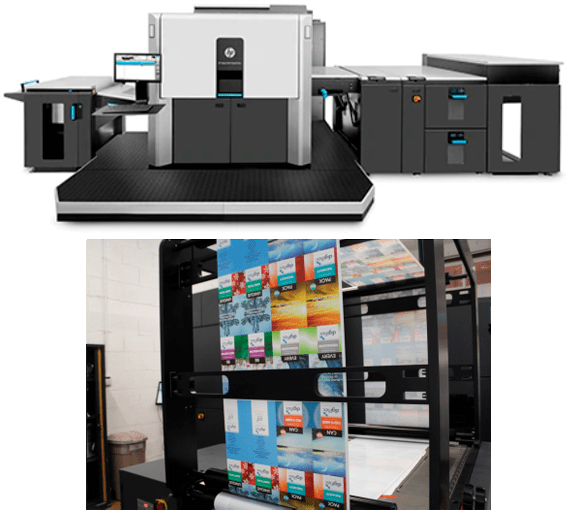
What is Digital Printing?
Digital printing is the ability to print without the use of plates or other tooling process.
It uses a proprietary printing process which is similar to the process used in laser printers, but with special electrostatically charged inks instead of toner, and without using a fuser, using instead a heated transfer roller to melt the charged ink particles before applying them to the substrate.

What is Extrusion?
The process of forming a thermoplastic by forcing the polymer melts through a shaped orifice. The extruded plastic is immediately chilled, and the resulting shape would be in the profile of the extrusion die.

What is Co-Extrusion (Co-Ex)?
The extrusion of two materials simultaneously from a single die in such a way that the two separate materials fuse together to form a single structure. The two materials still retain their individual properties except for the immediate contact area.
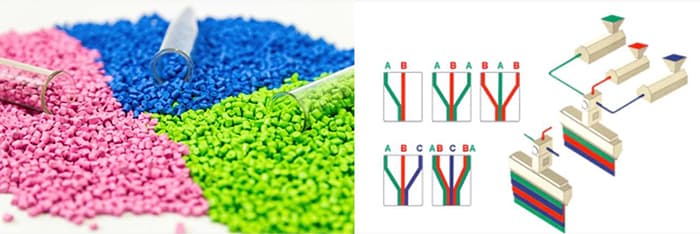
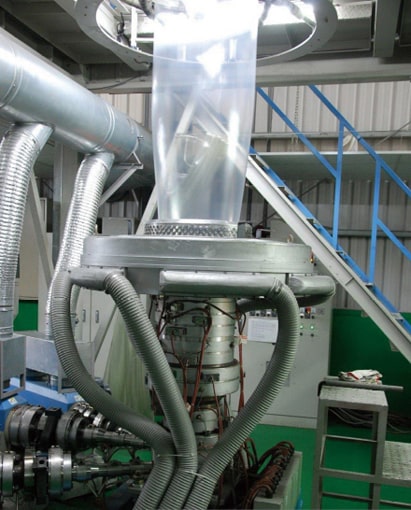
What is Blow- Film Extrusion?
The manufacture of thin plastic films by extruding a bubble of plastic and then inflating the bubble. In film manufacturing the extrusion and inflation are a continuous process.

What is Cast Film Extrusion?
A film that is extruded in a thin curtain from a slotted die and then cooled and solidified by being passed over a chilled roll.
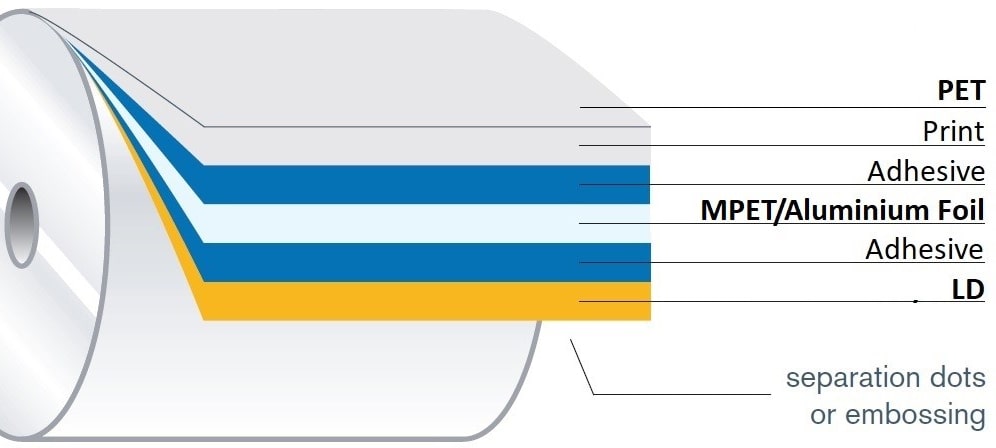
What is A Laminate?
A material composed of two or more layers of different materials, joined together to make a single sheet. The component layers may be applied coatings or other sheet materials bonded to the base material with adhesive substances.
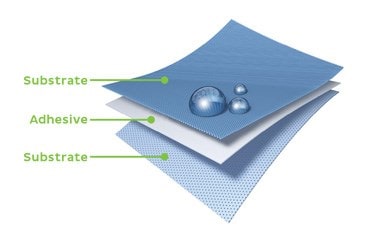
What is Adhesive?
A substance that can be used to join two surfaces. A typical adhesive is a liquid capable of forming molecular attractions to (wetting) the substrates and then solidifying by evaporation of volatile cooling, or chemical reaction.
What is A Barrier?
The ability to stop or retard the movement of one substance through another. In packaging, the term is most commonly used to describe the ability of a material to stop or retard the passage of atmospheric gases, water vapor, and volatile flavour and aroma ingredients.

What is Cold Seal?
A seal produce by an adhesive that adheres only to itself and requires only contact pressure to bond.
Ideal for heat sensitive products such as;
- Chocolates
- Ice creams




 sales@fmcpack.co.uk
sales@fmcpack.co.uk
 Fenn Corner, Rochester, Kent, ME3 8RF
Fenn Corner, Rochester, Kent, ME3 8RF